Cost Function in Machine Learning: Have you ever wondered how a machine learning model knows whether it’s learning the right thing or completely missing the mark? The answer lies in something called the cost function in machine learning. Think of it as a report card for your model, it shows how close or far the model’s predictions are from the actual answers.
In simple terms, if the cost is low, your model is doing well. If it’s high, your model still has a lot to learn. Without a cost function, training a machine learning model would be like shooting arrows in the dark, you’d never know if you’re hitting the target.
In this blog, we’ll explore the following:
- What is cost function in machine learning?
- The cost function formula in machine learning with an easy breakdown.
- The use of cost function in machine learning.
- Examples, including the cost function for logistic regression.
- How cost function gradient descent optimises models.
- Why this knowledge is vital if you’re exploring data science courses in Bangalore, online learning, or thinking about whether data science is a good career.
By the end, you’ll not only understand the math but also see why cost functions are at the heart of modern AI and data science.
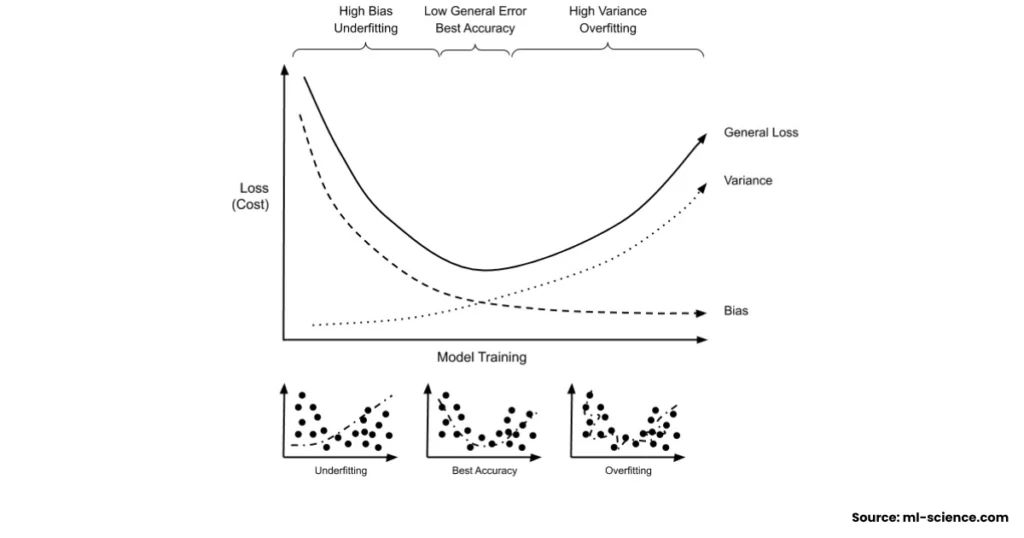
What is Cost Function in Machine Learning?
Let’s start with the basics: What is cost function in machine learning?
The cost function or loss function (sometimes also called an error function) is a mathematical expression that measures the difference between the model’s predicted output and the actual output. The smaller this difference, the better the model.
Imagine you’re learning to throw darts. Each dart you throw is like a prediction. The bullseye is the correct output. The cost function is the distance between your dart and the bullseye. The goal? Minimise that distance.
That’s exactly what the cost function helps us do; it provides a numerical value that quantifies errors so that the model can improve.
Read More: Machine Learning Projects For Final Year
Cost Function Formula in Machine Learning
The cost function formula in machine learning depends on the type of problem, regression, classification, etc. But one of the most common forms is the Mean Squared Error (MSE) for regression problems.
The formula is:
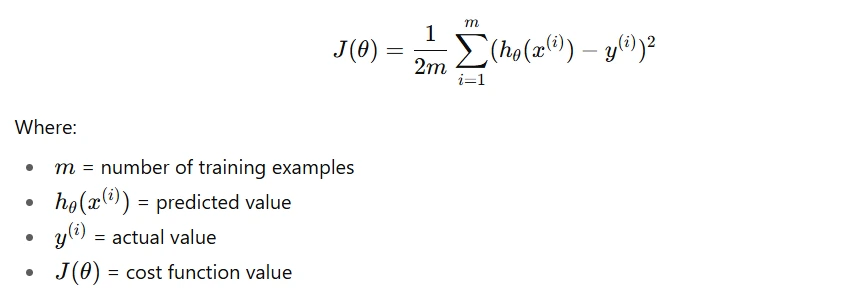
In plain language,
- Take the difference between the predicted and actual value.
- Square it (so that negative differences don’t cancel out positives).
- Average it over all examples.
This way, the cost function acts as a single number that shows how far off our model is from reality.
Use of Cost Function in Machine Learning
So, what’s the real use of cost function in machine learning?
- Model Evaluation: It tells us how well the model is performing.
- Optimisation: By minimising the cost function, we make the model better.
- Training Guidance: Algorithms like gradient descent use the cost function as a map to decide which direction to move in order to improve.
- Decision-Making: Whether it’s a simple regression or a deep neural network, the cost function decides when the model is “good enough.”
In short, the cost function isn’t just a mathematical tool, it’s the backbone of model training. Without it, data science and machine learning would have no way to measure progress.
Example of Cost Function in Machine Learning
Let’s work through a simple example of cost function in machine learning, shall we?
Suppose you’re building a model to predict house prices.
- Actual prices: [100, 200, 300]
- Predicted prices: [110, 190, 290]
Now, using the Mean Squared Error formula:
- Calculate errors: (110-100), (190-200), (290-300) → 10, -10, -10
- Square them: 100, 100, 100
- Average: (100+100+100)/3 = 100
So, the cost function value is 100.
This means, on average, the model is making an error equivalent to 10 units. The smaller this value, the closer we are to accuracy.
Cost Function for Logistic Regression
When it comes to classification problems, the cost function for logistic regression takes a different form because we deal with probabilities. And the formula is as follows:
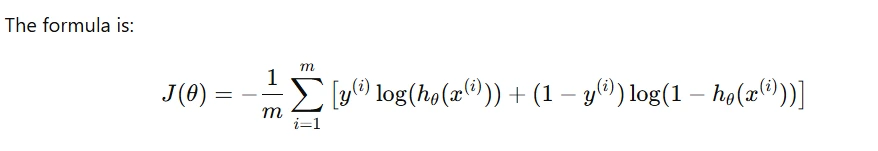
This may look complex, but here’s the essence:
- If the model predicts correctly, the cost is close to 0.
- If it predicts wrongly, the cost shoots up.
That’s why logistic regression is so popular, it’s efficient, reliable, and works well with binary classification tasks.
Cost Function Gradient Descent
You might be wondering: once we have the cost function, how do we reduce it?
That’s where cost function gradient descent comes in. Gradient descent is an optimisation algorithm that adjusts the model parameters step by step to minimise the cost function.
Picture yourself standing on a hill (the cost function curve). Your goal is to get to the lowest point (minimum error). Gradient descent is like taking small steps downhill in the direction of steepest descent.
Each step reduces the cost function value until you reach the lowest point possible. That’s when the model is trained.
Cost Function vs Loss Function – Are They the Same?
Here’s an interesting point that often confuses beginners: Are cost function and loss function the same?
Yes, in the context of machine learning and AI, the terms cost function and loss function are often used interchangeably. Both refer to a mathematical function that measures the error or “cost” of a model’s predictions compared to the actual values.
However, there’s a subtle difference worth noting:
- Loss function: Usually refers to the error calculated for a single training example.
- Cost function: Typically refers to the average of all loss values across the dataset.
For example, if you predict the price of one house and compare it to the actual price, that error is the loss. When you take the average of such losses across thousands of houses, that average is the cost function.
In practice though, data scientists and researchers often use both terms loosely. The main goal is the same: minimising these values during training to make the model better.
Why Cost Function Matters in Data Science?
At this point, it’s clear that cost functions aren’t just theory, they’re the core of model training. And since machine learning is a fundamental part of data science, understanding cost functions is a must for anyone aspiring to build a career in this field.
If you’re exploring data science courses in Bangalore, or looking for the best data science courses online, this topic will be one of the first things you’ll encounter. Many data science course for beginners programs start with concepts like cost function because they form the foundation for everything that follows.
And here’s the big question many ask: Is data science a good career?
The answer is yes, India and the world are seeing a surge in demand for skilled data scientists. From finance to healthcare to technology, every industry relies on data. Mastering concepts like cost functions gives you the technical edge that employers value.

At Zenoffi E-Learning Labb, two specialised programs, basic Data Science Course (Diploma) and Data Science & Generative AI Program, covers such topics step by step. They’re designed to help learners build a strong foundation before moving into advanced machine learning and AI concepts.
On A Final Note…
The cost function in machine learning may sound mathematical, but it’s essentially the feedback system that makes models intelligent. Without it, training models would be blind. From regression to classification, from beginner-friendly examples to complex neural networks, the cost function is the hidden force shaping accurate predictions.
And whether you call it a loss function or a cost function, the goal is always the same: minimise the error and make the model smarter.
If you’re aiming to enter the world of AI and data science, mastering this concept will set you apart. And if you’re looking to take the next step, exploring the best data science courses, be it data science courses in Bangalore or flexible online options, will give you the structured path you need.
After all, as the saying goes:
“Data is the new oil, but it’s the refining, through concepts like cost functions that makes it valuable.”
FAQs
1. What is cost function in machine learning in simple terms?
It’s a number that shows how far your model’s predictions are from the actual answers. Smaller the number, better the model.
2. Why is the cost function important?
Because it guides model training, it tells us if we’re improving or not.
3. Can you give an example of cost function in machine learning?
Yes, predicting house prices and calculating average squared errors is a basic example.
4. What’s the difference between cost function and loss function?
The loss function refers to the error for a single data point, while the cost function is the average error over all data points.
5. Is data science a good career in India?
Absolutely. With companies across sectors looking for data-driven insights, data science has become one of the most in-demand career paths.
6. What’s the best way to start learning data science?
Enrolling in structured programs like data science courses in Bangalore or online beginner-friendly programs is the best approach. For example, Zenoffi E-Learning Labb offers tailored learning paths for beginners and advanced learners.





