If you have ever wondered why machines can decide which question to ask next, you are already touching upon entropy in machine learning. The concept comes from information theory, and in simple terms, entropy measures uncertainty or randomness in data. It plays a major role in algorithms like Decision Trees, ID3, and Random Forests.
Claude Shannon, known as the father of information theory, once said:
“Information is the resolution of uncertainty.”
But how does this concept work in practice? How can you calculate it? And why does it matter for training efficient models? Let’s explore all of that in this blog, in the most simplified manner!
What Is Entropy in Machine Learning?
Entropy refers to the measure of disorder or impurity in a dataset. When data has high randomness (example: equal number of positive and negative examples), it has high entropy. When data is well-separated and pure (example: all are positive samples), it has low entropy.
In simple words:
- If the dataset is mixed, entropy is high.
- If the dataset is uniform, entropy is low.
- In terms of decision trees, entropy helps in deciding which attribute offers the best information gain.
For example, when splitting data in a decision tree, the algorithm uses the entropy formula in machine learning to calculate uncertainty before and after a split. The goal is always to reduce entropy and increase information gain.
The Entropy Formula in Machine Learning
So, what exactly is the entropy formula in machine learning? The mathematical representation is as follows:
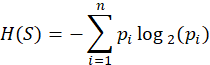
Where:
- H (S) is the entropy of the dataset S
- pi represents the probability of class i
- log2 is used since the unit of information is bits
This entropy equation machine learning framework helps the algorithm assess how homogeneous or diverse the dataset is.
Let’s put that into context with an example, shall we?
How to Find Entropy in Machine Learning: Example
Imagine a dataset designed to classify whether a student will pass or fail based on whether they study. Suppose 8 students passed and 8 failed. So, p(pass)=0.5 and p(fail)=0.5.
Using the entropy formula:
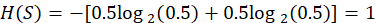
- This means the dataset is highly uncertain, the entropy is maximum.
- If all students had passed, then then p(pass)=1 and p(fail)=0, leading to H(S)=0.
- That means no uncertainty, or perfect purity.
This simple example shows how to find entropy in machine learning using basic probability.
Using Entropy to Build Decision Trees
Entropy in machine learning is central to information gain, which drives how decision trees are built. The idea is:
The more the entropy decreases after a split, the better that feature separates the data.
Information Gain (IG) is calculated as:
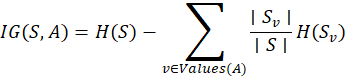
Here:
is the entropy before the split.
is the entropy after the split for value
of attribute
.
By comparing the IG of each attribute, the algorithm picks the best attribute to split the data on. That’s how algorithms like ID3 and C4.5 work under the hood.
By comparing the IG of each attribute, the algorithm picks the best attribute to split the data on. That’s how algorithms like ID3 and C4.5 work under the hood.

Why Entropy Matters in Machine Learning?
Now that we know the formula, why exactly does entropy in machine learning matter?
Let’s break it down:
- It quantifies uncertainty by helping the system measure how mixed or pure the data is.
- It drives learning decisions, particularly in models like decision trees and classification tasks.
- It helps identify feature importance, attributes that reduce entropy the most are often powerful predictors.
- It aids interpretability, entropy-based splits make decision trees easy to explain and visualise.
Entropy is not limited to trees. Many unsupervised learning models and information theory-based techniques also rely on similar principles.
Entropy Problems in Machine Learning
In projects, entropy problems in machine learning arise when datasets are imbalanced or noisy. For example:
- When one class dominates others, entropy values get skewed.
- When data contains too many uncertainties (like missing labels), entropy becomes less meaningful.
- If a model keeps selecting attributes that barely reduce entropy, it may lead to overfitting.
To handle such entropy problems in machine learning, practitioners often use:
- Data balancing techniques (like SMOTE)
- Regularisation methods
- Cross-validation to validate entropy-based splits across samples
Remember, entropy helps the model make smarter decisions, but it works best when given high-quality and balanced data.
How to Apply Entropy in Everyday ML Tasks?
Let’s see some places where entropy is used across ML workflows:
- Feature Selection: Choosing the feature that gives maximum information gain.
- Classification Problems: Understanding purity of data at each decision node.
- Clustering Models: Assessing diversity of cluster members.
- Unsupervised Learning: Measuring randomness when no labels are present.
Think about it this way, wherever there is uncertainty, entropy in machine learning finds relevance.
Read More: OpenAI CEO Praises Perplexity AI CEO | What Sam Altman’s Words Mean for the AI Community
Entropy and Information Gain: How Are They Different?
| Term | Meaning | Relation to Decision Trees |
| Entropy | Measures disorder in the data. | Represents uncertainty before splitting. |
| Information Gain | Reduction in entropy after a split. | Decides the best feature to divide data. |
As you can see, one cannot talk about entropy in machine learning without discussing information gain, they work like two sides of the same coin. When working with datasets in Python, you can calculate entropy using libraries like scikit-learn or NumPy. For example:
from math import log2
def entropy(p_list):
return -sum ([p * log2(p) for p in p_list if p > 0])
print (entropy([0.5, 0.5])) # Output: 1.0
This small snippet demonstrates how to find entropy in machine learning practically and efficiently.

On A Final Note…
Imagine tossing a coin, the entropy is highest when tails and heads have equal probability (0.5 each). If the coin is biased and always lands heads, the entropy becomes zero, since there’s no surprise in the outcome. And this is how entropy in machine learning helps machines quantify surprise and decision quality.
Theory to practice, entropy in machine learning remains one of the most powerful ideas driving intelligent decision-making. It tells a machine how “confused” it is and guides it to reduce that confusion step by step. If you ever find yourself asking what is entropy in machine learning, just remember: it’s a measure of surprise. The less the surprise, the smarter the model becomes.
FAQS
1. What is entropy in machine learning in simple terms?
Entropy measures how mixed or uncertain a dataset is. High entropy means more confusion; low entropy means a clearer pattern.
2. How to find entropy in machine learning datasets?
Use the Shannon entropy formula to calculate probabilities of classes and sum them using the entropy equation.
3. What is the role of entropy formula in machine learning algorithms?
It helps determine how pure or impure subsets of data become after splitting in a decision tree.
4. Why do entropy problems in machine learning occur?
They happen due to uneven class distribution, missing data, or excessive complexity in decision nodes.
5. How can entropy equation machine learning models be optimised?
By combining entropy reduction with information gain to focus on attributes offering maximum clarity.





