KDD vs data mining often confuses beginners in data analytics courses. Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD) forms the full pipeline to turn raw data into actionable insights, while data mining acts as one step within it. Understanding this distinction helps analysts handle large datasets from e-commerce or finance effectively.
This blog breaks down KDD vs data mining, highlighting their roles in data analytics. It defines each term, presents KDD vs data mining difference with a table, covers the KDD process steps, discusses the famous KDD Cup 99 dataset, explores data mining versus knowledge discovery in databases, and more.
What is Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD)?
Knowledge Discovery in Databases, or KDD, describes the entire process of extracting useful patterns from vast amounts of data. It goes beyond simple analysis to produce knowledge that guides decisions, involving multiple stages from data preparation to final interpretation.
Usama Fayyad, Gregory Piatetsky-Shapiro, and Padhraic Smyth defined KDD in 1996 as “the non-trivial process of identifying valid, novel, potentially useful, and ultimately understandable patterns in data.” This iterative workflow suits the analytics processes where data comes messy and unstructured.
What is Data Mining?
Data mining focuses on applying algorithms to discover patterns, associations, or anomalies in prepared data. It forms the core technique within KDD, using methods like clustering, classification, or regression.
Think of it as the “search engine” phase: once data stands clean, data mining sifts for hidden gems. Data mining tasks include association rules for market basket analysis or decision trees for predictions. In practice, tools like Python’s scikit-learn handle this step seamlessly.
KDD vs Data Mining Difference
When people search for data mining versus knowledge discovery in databases, they seek clarity on scope. KDD encompasses the broad journey; data mining targets pattern extraction.
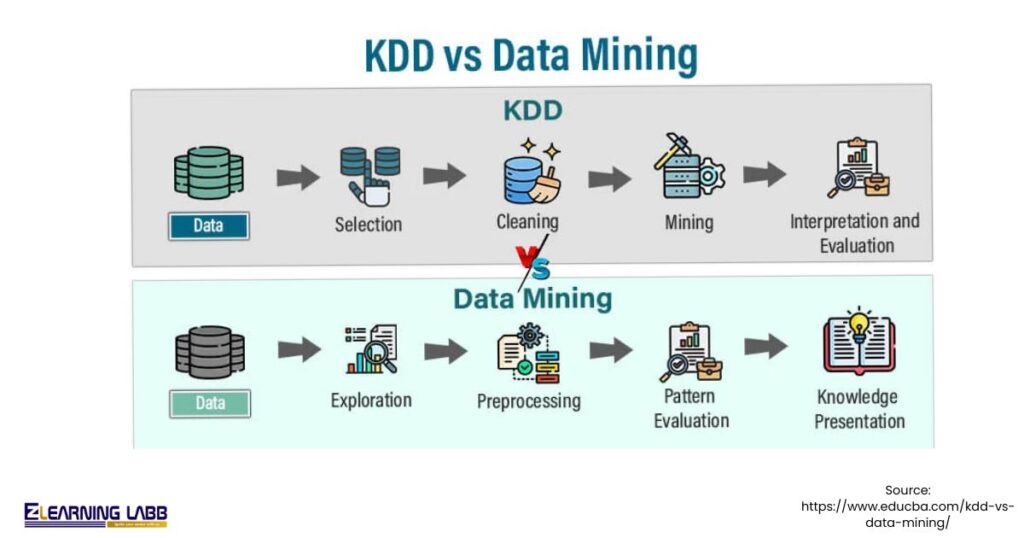
This table highlights how KDD wraps around data mining. Fayyad’s paper proves KDD’s broader view leads to more reliable results.
| Aspects | KDD (Knowledge Discovery in Databases) | Data Mining |
| Scope | Encompasses the entire workflow from raw data selection to final knowledge interpretation and deployment. | Focuses narrowly on applying algorithms to extract patterns from prepared data. |
| Key Stages Involved | Includes selection, preprocessing, transformation, mining, evaluation, and presentation in a loop. | Centres on the mining core, such as classification, clustering, or regression. |
| Primary Output | Delivers validated, understandable knowledge integrated with domain context for decision-making. | Generates models, rules, or patterns that require further evaluation. |
| Level of Iteration | Highly iterative across all phases, with feedback loops based on business needs and results. | Iterative mainly within algorithm tuning, but limited to the mining phase. |
| Role of Human Expertise | Relies extensively on domain knowledge for goal-setting, cleaning, and validation throughout. | Depends less on humans; more algorithm-driven once data stands ready. |
| Typical Tools | Combines preprocessing (Pandas), mining (scikit-learn), and visualisation (Matplotlib/Tableau). | Specialised algorithms like Apriori for associations or k-means for clusters. |
The KDD Process: Step-by-Step
The KDD process unfolds in a logical sequence of nine steps, often grouped for simplicity, making it adaptable to datasets of any scale.
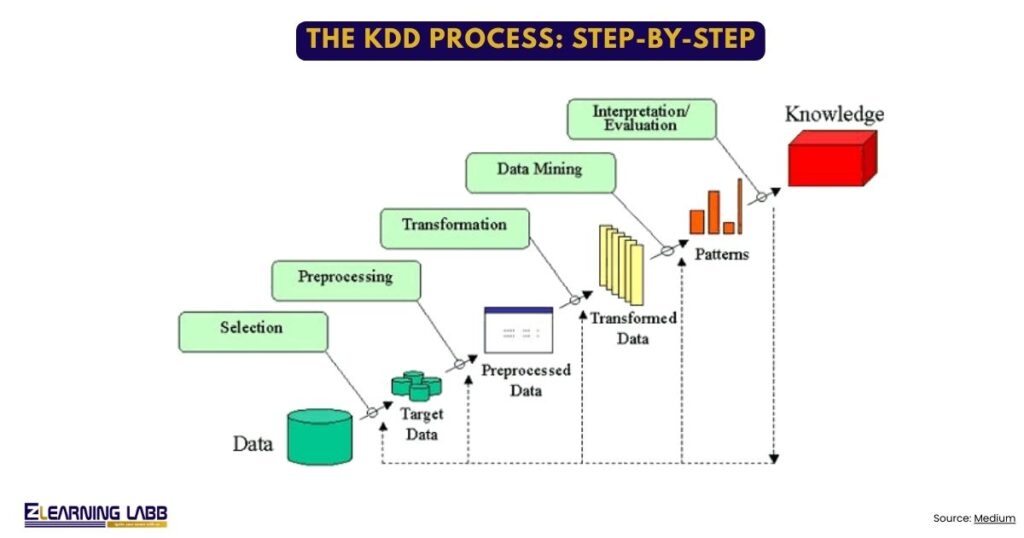
- Developing an Understanding of the Application Domain: Teams first define business objectives, such as predicting sales drops, and assess available data sources to align goals with reality.
- Creating a Target Data Set: Analysts select relevant subsets from warehouses or lakes, filtering by relevance to avoid overwhelming volumes common in Indian enterprise data.
- Data Cleaning and Preprocessing: This tackles noise, missing entries, and outliers through techniques like imputation or normalisation, ensuring downstream mining succeeds.
- Data Reduction and Transformation: Methods like dimensionality reduction via PCA or feature scaling condense data while preserving essence, speeding up analysis.
- Choosing the Data Mining Task: Decide on classification for labelling or clustering for grouping based on the problem at hand.
- Data Mining Itself: Here algorithms run to spot patterns, forming the bridge to knowledge.
- Interpreting Mined Patterns: Visualise results via charts or reports to check understandability.
- Consolidating Discovered Knowledge: Consolidate into reports or models ready for action.
Data Mining in the KDD Context
Data mining slots as the fourth stage in KDD. It thrives on clean data, employing:
- Classification for spam detection.
- Clustering for segmenting users.
- Association for recommendation engines.
Without prior KDD steps, results mislead. Data mining without preprocessing is like cooking with dirty ingredients.
KDD Cup 99 Dataset: Example
The KDD Cup 99 dataset benchmarks intrusion detection systems. Derived from DARPA 1998 data, it includes network traffic with normal and attack types like DoS or probe.
Features: 41 attributes (duration, protocol, etc.), 5 million training records. Despite age, it trains models for cybersecurity analytics.
On A Final Note…
In e-commerce giants like Flipkart, KDD pipelines forecast demand holistically, while data mining spots buying patterns within. Finance sectors apply them for risk models, and telecoms for churn analysis.
- KDD shines in end-to-end projects needing business alignment, like retail trend forecasting.
- Data mining excels in quick pattern hunts, such as A/B test insights.
Mastering KDD vs data mining builds strong foundations for analytics roles. With NASSCOM projecting 11 million jobs by 2026, skills in this shine in interviews.
What defines the core KDD vs data mining difference?
KDD covers the full process from data prep to knowledge deployment, while data mining handles just the pattern extraction step within it.
Where can I find KDD vs data mining in tabular form?
Refer to the comparison table above, which contrasts scope, steps, outputs, and more side by side.
What makes the KDD Cup 99 dataset significant?
It serves as a standard benchmark for network intrusion detection, featuring millions of labelled traffic records for training KDD pipelines.
How does data mining versus knowledge discovery in databases play out?
Data mining extracts raw patterns algorithmically; knowledge discovery in databases wraps it in preprocessing and evaluation for usable insights.
Does data mining form part of the KDD process?
Yes, it acts as the central mining stage after cleaning and transformation but before evaluation.





