Artificial intelligence and machine learning are often described as the backbone of modern technology, be it from voice assistants to self-driving cars. But what makes machines learn and make decisions? The answer lies inside a neural network, inspired by how our human brain works.
In this blog, we will simplify single layer vs multilayer neural network, explain how each function, highlight their advantages, and explore some examples for your quick and easy understanding.
Table of Contents
- What is a Neural Network?
- What is Single Layer Feed Forward Neural Network?
- Moving to Multilayer Neural Network in Machine Learning
- Single Layer vs Multilayer Neural Network
What is a Neural Network?
A neural network is a series of algorithms designed to recognize patterns. It works by processing data through layers of interconnected “neurons.” Each neuron receives input, performs a weighted calculation, passes it through an activation function, and then sends the output to the next layer.
This layered structure allows neural networks to learn from examples, much like how humans learn from experience.
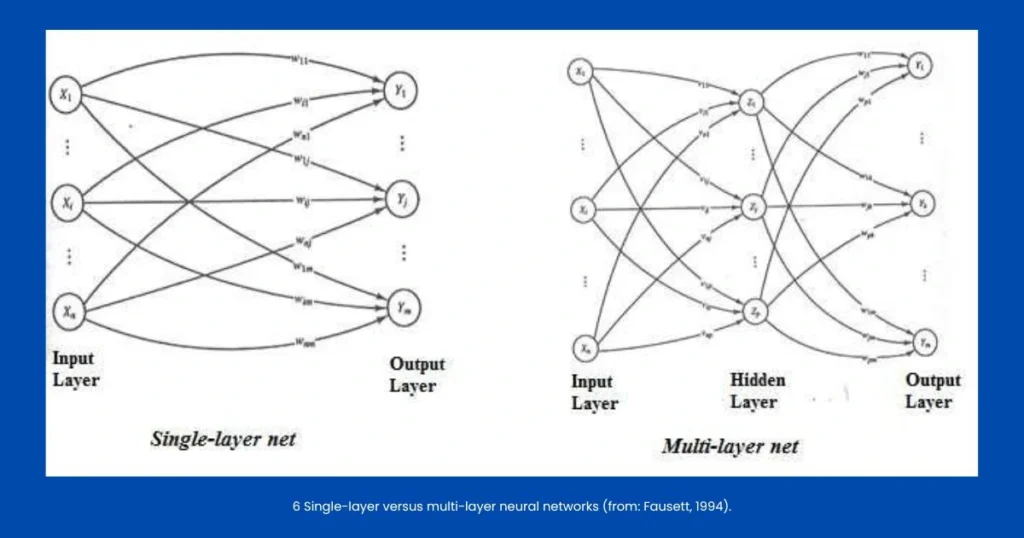
What is Single Layer Feed Forward Neural Network?
Let’s begin with the simplest type, and that is, the single layer feed forward neural network. In this model, information moves only in one direction, from the input layer to the output layer. There are no loops or feedback mechanisms. This is why it’s called feed forward.
- Structure: It has one input layer and one output layer.
- Computation: Each input node is connected to every output node with a specific weight.
- Learning: It uses algorithms like the perceptron learning rule.
The single layer perceptron in neural network is the most basic form of this model. It was introduced by Frank Rosenblatt in the late 1950s and could only classify linearly separable data, for example, distinguishing between two classes based on a straight-line boundary.
What Is Neural Network In Machine Learning? Must Know For Data Scientists
“A perceptron can learn any binary function that is linearly separable,” stated Rosenblatt in his early papers, which shaped the foundation of neural network theory.
So, while a single layer feed forward neural network is great for simple classification tasks, it falls short when the data becomes complex or non-linear, a limitation that led to the creation of multilayer networks.
Moving to Multilayer Neural Network in Machine Learning
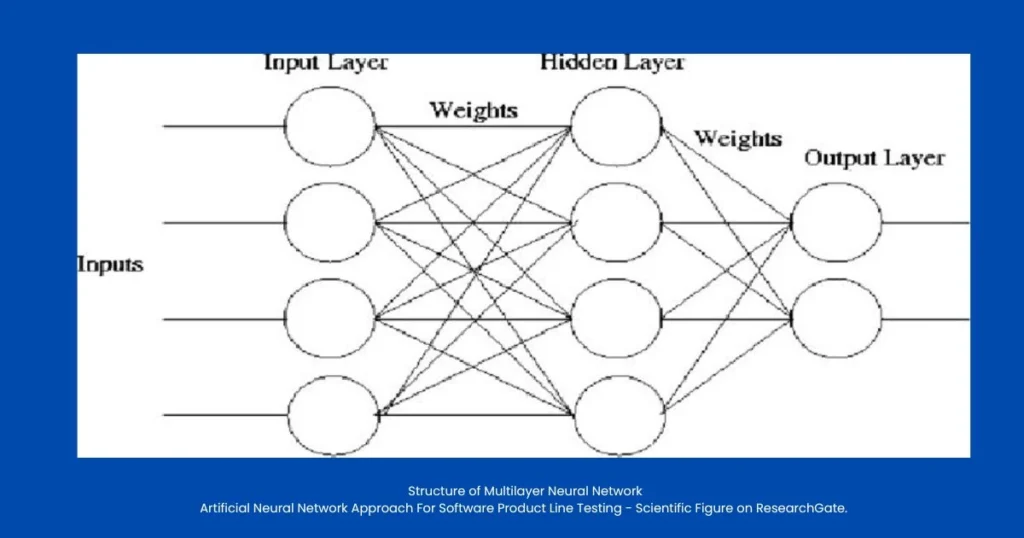
A multilayer neural network in machine learning adds more depth and power to the structure. Instead of just one layer, it includes one or more hidden layers between the input and output layers. These hidden layers allow the system to capture complex, non-linear relationships in the data.
This type is commonly known as the Multilayer Perceptron (MLP).
Structure and Function
- Input layer: Receives the raw data.
- Hidden layer(s): Performs intermediate transformations using activation functions such as ReLU, Sigmoid, or Tanh.
- Output layer: Produces the final prediction or classification.
The process of training a multilayer perceptron neural network example often involves the backpropagation algorithm. It fine-tunes weights by minimizing the error between predicted and actual outputs.
As Geoffrey Hinton, often called the “Godfather of Deep Learning,” said, “Adding hidden layers allows neural networks to extract higher-level features, making learning more powerful.”
Single Layer vs Multilayer Neural Network
When comparing single layer vs multilayer neural network, think of it as comparing a straight line to a series of curves, one is simple and direct, while the other can represent complex shapes.
Here’s a clear distinction between the two:
| Aspect | Single Layer Neural Network | Multilayer Neural Network |
| Layers | Only one layer between input and output. | Multiple layers (hidden + output). |
| Computation Type | Simple linear mapping. | Complex, non-linear mapping. |
| Learning Algorithm | Perceptron learning rule. | Backpropagation and advanced optimizers. |
| Suitability | Linearly separable problems. | Non-linear and complex problems. |
| Speed | Fast but limited. | Slower but more accurate. |
| Applications | Basic classification tasks. | Image recognition, NLP, forecasting, etc. |
How Multilayer Networks Replaced Single Layer Models
Have you ever wondered why researchers moved from single layer to multilayer networks?
The answer lies in data complexity. Data is rarely linear, images, speech signals, and even financial data have nonlinear patterns. A single layer network cannot model such dependencies. On the other hand, a multilayer neural network in machine learning can model intricate features through deeper layers, each layer learning a specific level of abstraction.
For example:
- The first hidden layer might identify edges in an image.
- The second might detect shapes.
- The third could identify entire objects.
- This hierarchy of feature learning is what gives modern neural networks their strength.
Multilayer Perceptron in Action: Example
To make this concept clearer, let’s look at a multilayer perceptron neural network example in a simple classification task.
Imagine you are training a model to recognize handwritten digits from the MNIST dataset.
- Input: Pixel values from digit images.
- Hidden Layers: Apply activation and weighting computations.
- Output: Predict a digit (0–9).
When using, a single layer perceptron in neural network would fail because the relationship between pixel intensity and the digit pattern is highly non-linear. But a multilayer neural network in machine learning successfully handles it with multilayer representations.
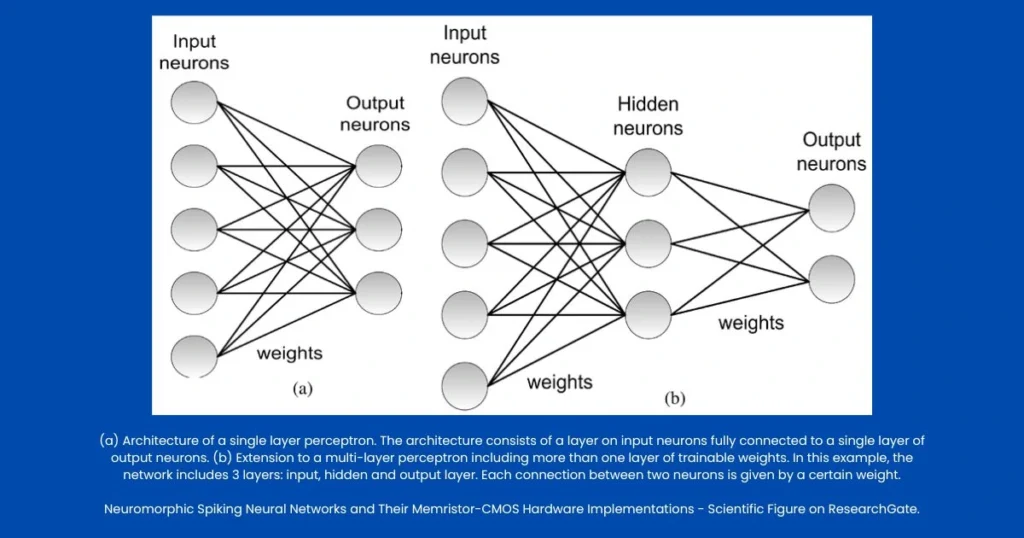
Advantages and Limitations
Every neural network architecture has its strengths and trade-offs. Understanding these helps select the right model for your machine learning problem.
Single Layer Feed Forward Neural Network: Advantages
- Simple and fast to train: Because it has only one computational layer, training involves fewer parameters, making the model lightweight and efficient.
- Good for linearly separable datasets: Performs well when input data can be divided with a straight line or a linear boundary, such as basic classification problems.
- Low computational cost: Requires minimal hardware resources and can even run comfortably on standard computing systems without GPUs or high-end processors.
Single Layer Feed Forward Neural Network: Limitations
- Cannot learn non-linear relationships: Struggles with data patterns that are curved, clustered, or interdependent, as it lacks hidden layers to model complexity.
- Not suitable for complex problems: Most data, like speech, images, and financial signals, is inherently non-linear, making the single layer model inadequate for such tasks.
Multilayer Neural Network: Advantages
- Can handle non-linear data: Hidden layers and activation functions allow the model to learn complex, non-linear mappings between input and output.
- Suitable for complex tasks like speech recognition and image classification: Powers applications that require understanding patterns within large, unstructured datasets.
- Supports deep learning when more layers are added: Forms the foundation of deep learning architectures where multiple layers enhance abstraction and pattern recognition.
Artificial Neural Network in Machine Learning: Working And Types
Multilayer Neural Network: Limitations
- Requires high computational power: Training deep or wide networks demands GPUs, large memory, and longer processing times.
- Prone to overfitting if not regularised properly: Without techniques like dropout, early stopping, or proper validation, the model may fit too closely to training data and fail on unseen data.
On A Final Note…
The debate on single layer vs multilayer neural network reflects the evolution of learning systems, from simple linear classifiers to today’s deep neural architectures.
If you’re starting in machine learning, begin with a single layer feed forward neural network to understand the basics. Then move to multilayer neural network in machine learning for more complex tasks.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between single layer and multilayer neural network?
A single layer network has no hidden layers and can only learn linear relationships, while a multilayer neural network includes hidden layers that allow it to learn complex, non-linear patterns.
2. Is single layer feed forward neural network still used in AI?
Yes, it’s still used for simple and linearly separable problems, especially in academic tutorials or small-scale automation projects.
3. Why is multilayer perceptron more powerful?
Because it uses multiple hidden layers to learn hierarchical patterns from raw data through backpropagation.
4. Can single layer perceptron learn non-linear data?
No, it cannot. Non-linear data requires multiple layers for efficient learning.
5. What are some multilayer perceptron neural network examples?
Digit recognition, image classification, sentiment analysis, and stock prediction models are classic multilayer perceptron neural network examples.





